We talk about ‘good data in, good data out’ for successful market research. We can apply the same theory to online survey design and say, ‘good question in, good answer out’.
When creating an online survey, often the focus is on writing the questions and establishing the order. However, choosing the right question type is also important, to ensure you collect reliable and honest responses that ultimately guide your business decisions.
Question types can influence data returns now more than ever, with the increase of survey taking on smartphones. The way a person interacts with a survey question on a smartphone is different than the way they do on a desktop.
Not adapting for mobile responders or the nuances of mobile devices can lead to surveys that are overly long, repetitive, confusing, or frustrating for respondents. Using question types in the right way at the right time will positively impact engagement and response consideration in a more natural way.
While there are many techniques that can be used to improve the survey experience for online respondents, we answer three common questions regarding question types here.
1. When should I use grids or scales in an online survey?
Banks of iterative questions are frequently displayed using grid or slider question types. Common uses might include:
- Establishing how often/recently a person bought a product or used a service
- Determining how much a person would recommend a brand to friends and family
- Understanding how much a person would agree (or disagree) with a particular statement
Accommodating for mobile
To accommodate respondents answering on their smartphone, it is essential that the alignment of the scaled options fits neatly on the screen without the need for horizontal scrolling. This typically requires displaying one “row” at a time and aligning the options vertically when it’s not possible to display them legibly horizontally.
Although it may be necessary for your research to focus on one row at a time, such questions can be repetitive and frustrating for respondents. Frustration can lead to boredom, which often leads to increased dropout or poor data.
Potential bias
Likert scale questions can suffer from acquiescence biases. This is a tendency to slightly agree with statements (particularly in the absence of a strong opinion either way), which can lead to contradictory survey results. Where possible, try to limit the number of iterations of a scaled question to a maximum of 12-15 repetitions.
Alternatives to traditional grids and scales
Consider asking your grid or scale questions in a completely different way. For example, asking about the likeliness to purchase a range of 14 toothpaste products using drag and drop, rating scale questions or mulit-code question types.
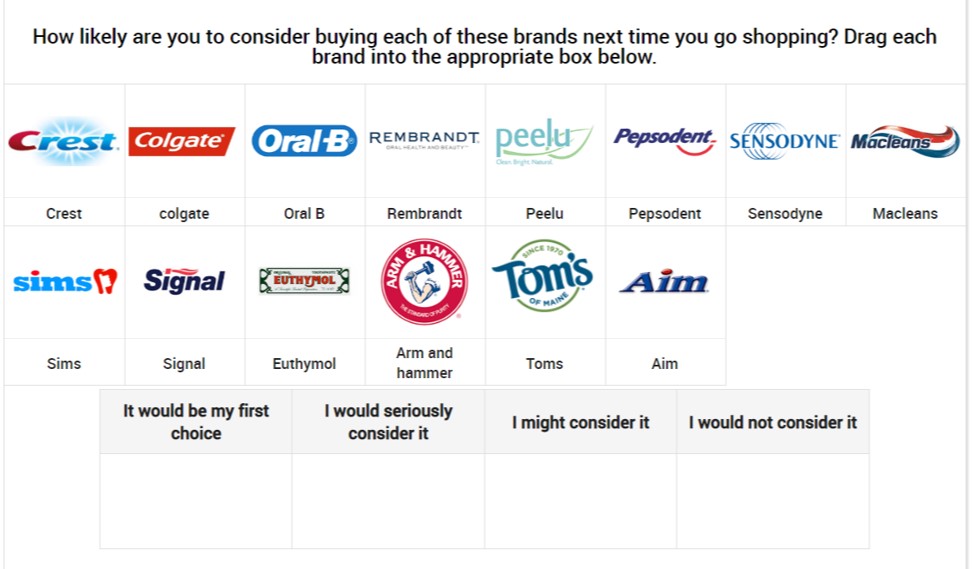
As seen above, you could ask respondents to drag and drop each brand to the appropriate box to indicate how likely they are to consider buying each.
However, this approach does not reflect how most people think about toothpaste when making a purchase – so a rating scale may be more appropriate.
People typically have specific brands that they would consider and specific brands they wouldn’t. Instead of the above question, replace the 14-iteration drag and drop with two simple questions shown below.
The first is a ranking question that tells us peoples’ first choice and other brands they would consider.

The second question is a multi-code which tells us the brands people would not consider. Any options not selected in these two questions are brands that the respondent might consider.

2. How many items should be in a list?
Keep lists in a question to 15 items or under. When you use a list longer than 15 items you run the risk of respondents not fully considering all options.
Respondents are more likely to click the first few items they see as relevant. This means you could introduce order bias into your data. This is especially relevant for surveys being taken on smartphones when scrolling is required. Typically order bias is reduced by randomizing the list order, but this may make choices harder for the respondent to process.
Tips for shortening lists
Firstly, ensure that every item in the list is absolutely necessary. Try to be strict with the choice of items that you are including. Ask the questions:
- Are there options that you expect almost everyone to select (and not tell you anything interesting)?
- Are there options that are very niche (and might not provide enough data)?
- Are all the items relevant to the respondent?
- Is there any duplication between list items?
Grouping lists
Once you have reduced the list items as much as possible, try breaking a single long list into smaller, logical groups. This allows respondents to focus on a subset of items, making it easier to consider all list items.
For example, asking a respondent about a wide range of activities they might engage with whilst listening to podcasts. Rather than asking these in a single randomized list, it would be preferable to group them in a logical way, such as “while…”, “with…”, and “in what moods…”.
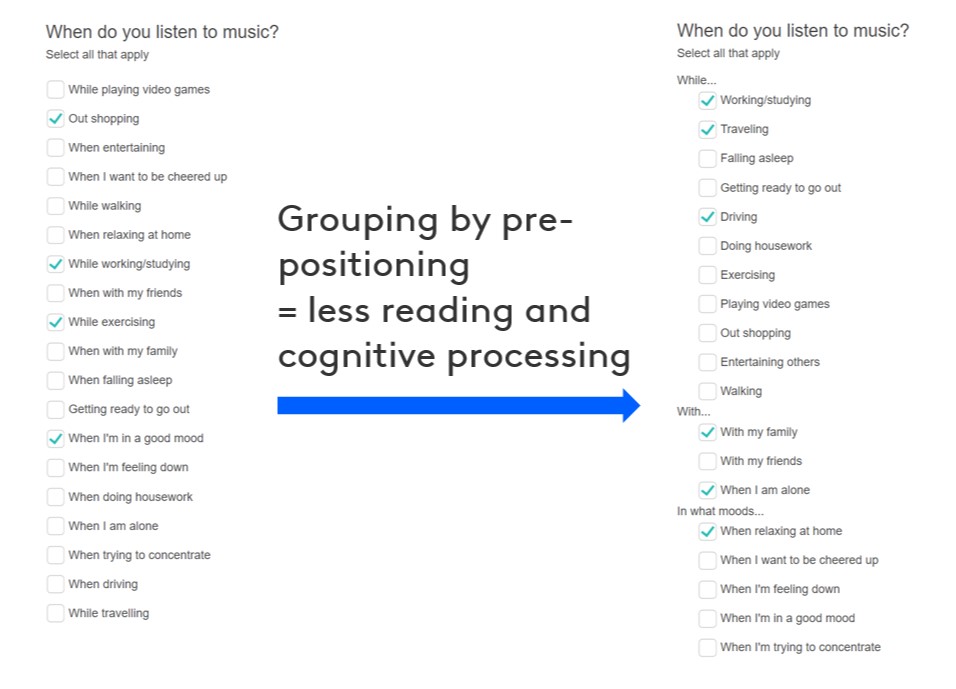
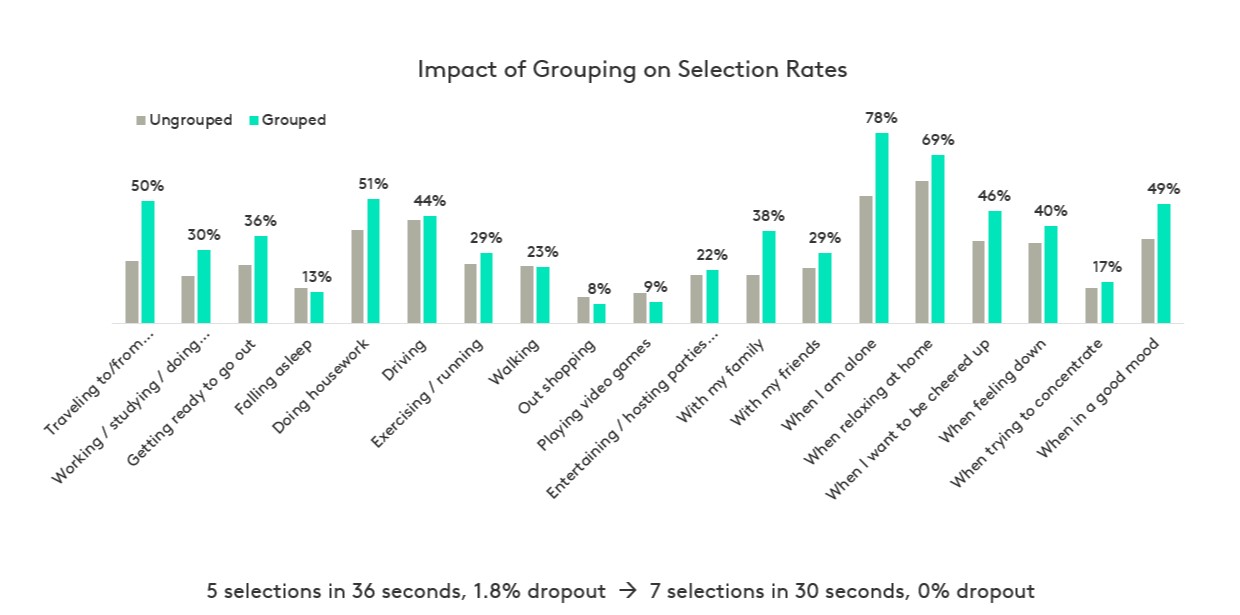
Kantar has found that grouping allows respondents to process long lists and answer the question more easily. This results in respondents providing more data in less time and with less frustration or dropout.
3. How should I ask open-ended questions?
Open-ended questions can provide rich survey data, but there are some factors that should be considered when using them.
Placement in the survey
Avoid asking open-ended questions near the beginning of a survey or asking two or more in quick succession. These questions present more of a challenge for smartphone users due to the size of the screen and the keypad.
Encountering open-ended questions too early in the survey or at too high a frequency can set a negative expectation with respondents, and lead to increased drop out or frustration.
Alternative approaches
One of the main uses of an open-ended question is to establish spontaneous or unprompted brand awareness. Sometimes there is a need to also establish “top of mind” awareness. This can lead to an initial question asking about a single brand, followed by a question asking for the names of other brands they can think of.
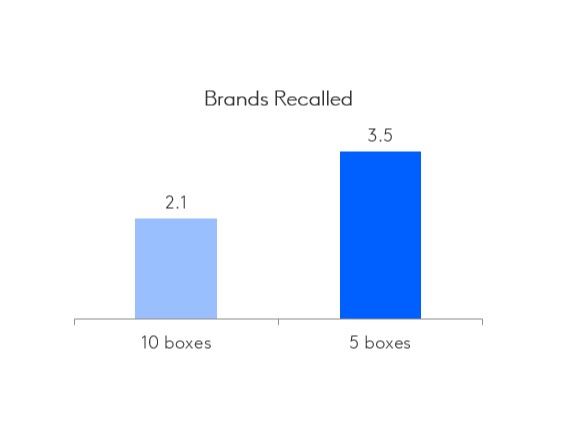
Instead of asking for a long list of brands, we recommend showing five boxes for the respondent to complete together and to treat the first text box as the top-of-mind mention. This removes the need for multiple questions and will help with engagement.
Kantar has also found that providing a limited number of text boxes encourages respondents to provide more entries.
Consider the below example.
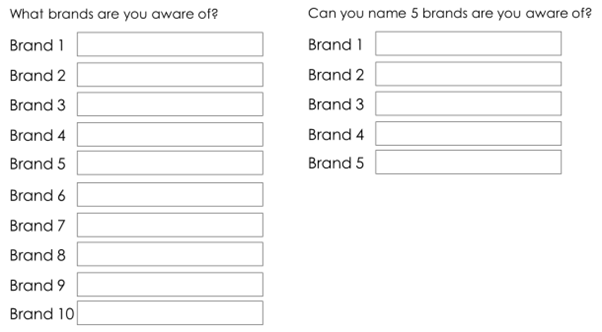
Because it is much more likely that naming five brands is reasonable and achievable, respondents tend to feel more motivated to enter more brands than if they are asked to provide up to ten. Also, asking “can you name five brands” vs “what brands are aware of”, creates a challenge for the respondent, rather than simply asking them to list brands.
Learn more
Through careful consideration of the right question type you can ensure you get the right data to inform your decisions.
Check out our Online Survey Design Modules for a deeper view of the design and use of different types of survey questions. You’ll find expert advice from Kantar in addition to research-on-research results.
Sign up using the form below to receive research tips on the first Thursday of every month. Topics include design, engagement, sampling and data enhancement. You’ll also be the first to hear when new Online Survey Training modules are released.



